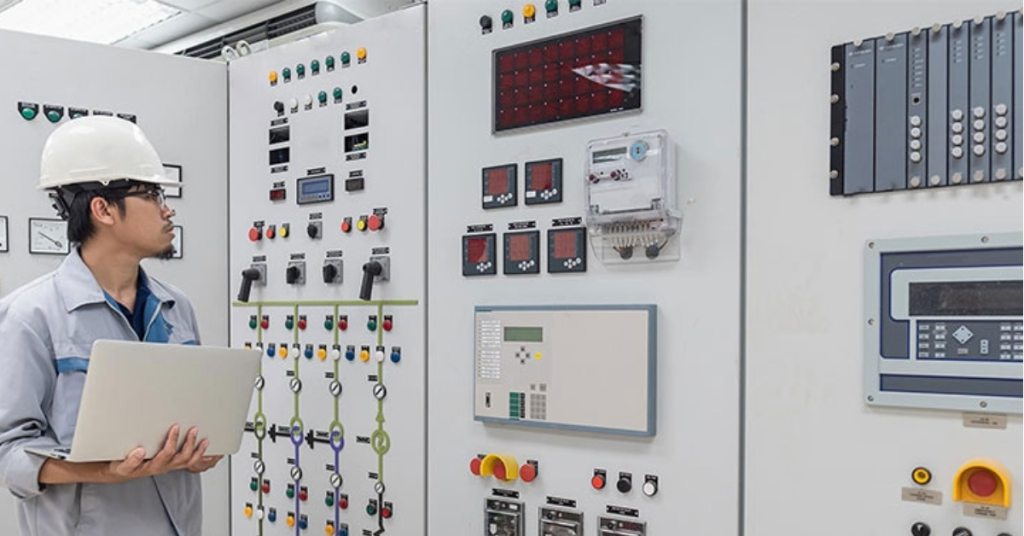

What is switchgear ?
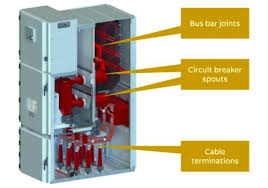
Switchgear contains fuses, switches, and other power conductors. However, circuit breakers are the most common component found in switchgear. During an electrical fault, a circuit breaker will sense the anomaly and interrupt the power flow, effectively limiting damage to the system.
Because it’s designed to control the flow of power, switchgear plays a role in enhancing a facility’s energy efficiency and safety.

Importance of Switchgear:
Switchgear is a critical component in electrical power systems, acting as the central control and protection point for electrical equipment. It’s essential for ensuring safety, reliability, and efficient power distribution in various settings, from homes to large industrial facilities.
Thus it equipment prevents damage and service interruptions by controlling the power flow within an electrical system. It can isolate affected circuits while concurrently supplying power from multiple sources to a load. When an electrical surge or fault triggers a circuit breaker within the electrical switching assembly, supporting components interrupt and exhaust the current in the overloaded circuit while maintaining service to operating circuits.
Here’s why switchgear is so important:
1. Safety:
- Protection against electrical hazards: It protects personnel and equipment from electrical faults like overloads, short circuits, and ground faults.
- Fault isolation:It isolates faulty sections of the electrical system, preventing damage to other equipment and minimizing the risk of injury.
- Emergency power shutdown: In hazardous situations, it allows for quick and safe disconnection of power.
2. Reliability and Efficiency:
- Consistent power supply: It ensures a stable and reliable power supply by quickly identifying and isolating faults, minimizing downtime.
- Efficient power distribution:It manages the flow of electricity, delivering power to the right areas of a facility or system.
- System maintenance:Switchgear allows for safe and controlled maintenance procedures by isolating specific sections of the electrical system.
3. System Control:
- Switching and control:Switchgear enables the switching and control of electrical circuits, allowing for the management of power flow.
- Remote operation:Modern switchgear can be operated remotely, providing flexibility and ease of control.
- Monitoring and measurement:Switchgear often includes metering and monitoring capabilities, allowing for the tracking of power consumption and system performance.
4. Applications:
- Industrial facilities:Switchgear is vital for controlling power distribution in factories, ensuring smooth operations and preventing costly downtime.
- Commercial buildings:It manages power distribution in offices, shopping centers, and other commercial spaces, ensuring a reliable power supply for essential services.
- Power generation and transmission:Switchgear plays a crucial role in power plants and substations, controlling the flow of electricity from generation to distribution.
- Residential:Low voltage switchgear protects homes from electrical hazards and ensures efficient power distribution.
In essence, switchgear is the backbone of Electrical systems, ensuring the safe, reliable, and efficient delivery of power.

Types of Switchgears
1. Miniature Circuit Breakers (MCBs)
MCBs are designed to protect electrical circuits from overloads and short circuits. These devices automatically disconnect the circuit when the current exceeds safe limits, preventing damage to wiring and connected devices. GreatWhite’s MCBs are known for their high performance, current-limiting capabilities and dual protection system, safeguarding against both thermal overloads and electromagnetic short circuits.
2. Residual Current Circuit Breakers (RCCBs)
RCCBs are crucial for preventing electrical shocks and fires caused by leakage current. They detect and disconnect the circuit if a leakage current is detected, ensuring the safety of both people and property. GreatWhite’s RCCBs are designed to provide reliable protection against earth leakage hazards, offering peace of mind in any electrical setup.
3. Residual Current Circuit Breaker with Overload Protection (RCBO)
RCBOs combine the features of an RCCB and an MCB, offering protection against both earth leakage and overload conditions. This makes them an essential part of modern electrical systems, ensuring that circuits are protected from both faults. GreatWhite’s RCBOs provide superior protection, making them ideal for both residential and commercial applications.
4. Distribution Boards (DBs)
Distribution Boards act as the central hub for electrical distribution in buildings. They house various protective devices like MCBs and RCCBs, ensuring the safe and organized distribution of electrical power. GreatWhite’s DBs are designed to meet high technical standards, providing flexibility, safety and ease of installation for a seamless electrical setup.
5. Isolators
Isolators are manually operated switches used to disconnect a part of an electrical circuit for maintenance or repair. These devices ensure that the circuit is completely de-energized, providing a safe environment for technicians to work. GreatWhite’s isolators are built to handle both normal and overload conditions, ensuring reliable performance in diverse applications.
6. Changeovers
Changeover switches are used to switch the load between two power sources, ensuring an uninterrupted power supply. These devices are commonly used in residential, commercial and industrial settings, providing a seamless transition between the main power supply and backup sources such as generators. GreatWhite’s changeover switches are designed for easy operation and exceptional reliability, keeping your power systems running smoothly.
7. Off-Load / On-Load Changeovers
Off-Load and On-Load changeovers are essential for managing power transitions between different sources. Off-Load changeovers are used when the system is de-energized, allowing for a safe switching process. On-Load changeovers, however, can operate while the power is still live, making them ideal for situations where uninterrupted power is critical. Both types of changeovers are designed to handle varying load requirements efficiently.
8. ACCL (Automatic Changeover Control System)
The Automatic Changeover Control System (ACCL) is an advanced mechanism used to automatically switch between power sources without manual intervention. In case of a power failure or disruption in the main supply, ACCLs automatically transfer the load to a backup power source, ensuring continuous operation. GreatWhite’s ACCL systems are engineered to provide fast, reliable switching to avoid any downtime in critical applications.
9. Molded Case Circuit Breakers (MCCBs)
MCCBs are robust circuit breakers designed for protecting electrical systems from overloads and short circuits. They offer adjustable trip settings and are ideal for higher currents and industrial applications. GreatWhite’s MCCBs are designed for durability and dependability, ensuring maximum protection for both commercial and industrial power systems.
Things to Keep in Mind When Selecting Switchgears
When selecting switchgears for your electrical system, consider the following factors:
Application Requirements: Ensure the switchgears meet the specific needs of your residential, commercial or industrial application.
Safety Standards: Choose switchgears that comply with relevant safety standards and regulations to avoid potential hazards.
Quality & Durability: Opt for high-quality switchgears that offer long-lasting performance and reliability.
Ease of Installation: Select switchgears that are easy to install and maintain, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
The type or voltage switchgear systems you need ultimately depends on the power load you have.
What is the difference between LV, MV and HV switchgear?
The three types are distinguished by their varying voltage levels, which is the primary difference between them. But what are the three different voltages used for?
Let’s start with low voltage switchgear first.
Low Voltage
Low-voltage switchgear can control systems up to 1kV in voltage. These are frequently used in a variety of industries and are typically found on the low-voltage sides of power-distribution transformers.
Medium-Voltage
Systems with voltages between 1kV and 35kV use medium-voltage switchgear. This switchgear is frequently used in systems that include transmission and distribution lines, generators, feeder circuits, and motors.
High-Voltage
Lastly, we have high voltage switchgear. A high-voltage switchgear system is one that can manage between 35 kV and 230kV of voltage. These breakers frequently have improved safety features because they are made for high-voltage use.


