The current power system deals with vast currents, for this a special attention has to be given to the designing of the circuit breaker to secure a break of the arc produced during the process of the circuit breaker. This is the fundamental definition of circuit breakers. These have been divided into various types based on special categories such as MCB and MCCB, ELCB & RCCB.
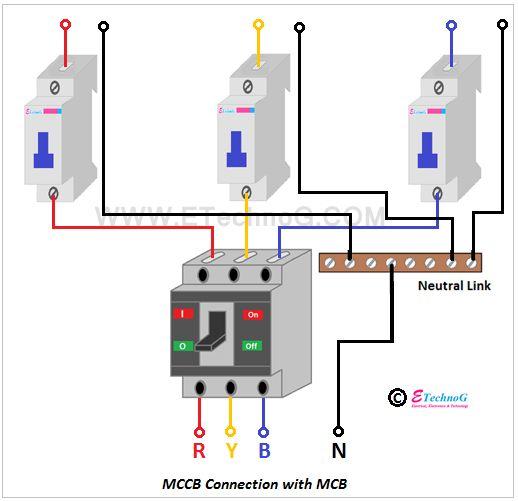
MCB (Miniature Circuit Breaker) and MCCB (Moulded Case Circuit Breaker) are both electrical protection devices that safeguard circuits from over currents and short circuits. The main differences lie in their current and voltage ratings, breaking capacity, and physical construction.

(Miniature Circuit Breaker):
- Current Rating: Handles lower current loads, typically up to 100 amps. The rated current is not a maximum of 125 amps
- Voltage Rating: Operates at lower voltages, suitable for residential and light commercial use.
- Breaking Capacity: Has a lower breaking capacity,
- Construction: Generally smaller and simpler in design.
- Applications: Commonly used in
- homes, offices, and small commercial buildings for protecting lighting circuits, power outlets, and small appliances.
MCB (Miniature Circuit Breaker):
- Current Rating: current rating of between 10 to 200 amperes. The uninterrupt rating is between 10k to 200k amperes
- Voltage Rating:It is also of low voltage to meet IEC947 standards and used for Heavy Commercial purpose.
- Breaking Capacity:
- Reflecting higher capacity
- Construction: Generally Medium to Advance design.
- Applications: Commonly play a key role in complex industrial electrical systems.
Key Differences Summarized:
| Feature | MCB | MCCB |
|---|---|---|
| Current Rating | Lower (up to 100A) | Higher (63A to 2500A+) |
| Breaking Capacity | Lower | Higher |
| Applications | Residential, light commercial | Industrial, large commercial |
| Construction | Smaller, simpler | Larger, more robust |
What exactly is MCB?

MCB is an abbreviation for Miniature Circuit Breaker. If there is an abnormal condition in the electrical network, such as an overload or a short circuit, it automatically shuts down the electrical circuits. The fuse, on the other hand, may detect these conditions, but it will need to be replaced even if it can be reset. Overcurrent protection is provided by the Miniature Circuit Breaker, which is an electromechanical device that protects the electric wires and electrical load from any type of fire or electrical hazard.
Handling an Miniature Circuit Breaker is relatively safe, and it restores power to the system in a short period of time. When it comes to overload and short circuit protection in residential applications, the miniature circuit breaker is the most popular choice. MCBs can be reset in a short period of time and do not require any maintenance. This type of circuit breaker operates on a bi-metal respective principle, which protects against overload current and solenoid short circuit current.
The working principle of the MCB
Because of the overflow of current that occurs through the – Miniature Circuit Breaker – the bimetallic strip becomes heated and deflects, resulting in bending. A latch is released as a result of the deflection of the bimetallic strip. The latch is responsible for turning off the MCB by preventing current from flowing through the circuit. This procedure helps to protect the appliances or devices from the dangers that can occur as a result of an overload or an overcurrent. Manually turning on the MCB is required in order to restart the flow of current.
During short circuit conditions, the current rises suddenly and in an unpredictable manner, causing the electromechanical displacement of the plunger associated with a solenoid to be displaced electromechanically. When the plunger strikes the trip lever, the latch mechanism is automatically released, resulting in the circuit breaker contacts being opened, which is a good thing.
Thus, an MCB function by interrupting the stability of electrical flow through the circuit once an error is detected. In simple conditions, this circuit breaker is a switch which routinely turns off when the current flows through it and passes the maximum acceptable limit. Generally, these are designed to guard against over current and overheating.
What exactly is MCCB?

Moulded Case Circuit Breaker is a type of electrical protection device that is used when the load current exceeds the limit of a miniature circuit breaker, which is another type of electrical protection device. The MCCB protects against overloads and short circuit faults, and it is also used to switch circuits when necessary. Even in domestic applications, it can be used for higher current ratings and fault levels due to its higher fault level.
It is in industrial applications that MCCBs are used because of their wide current ratings and high breaking capacity. They can be used for a variety of applications, including the protection of capacitor banks, generator protection, and the distribution of main electric feeders. It provides adequate protection whenever discrimination, adjustable overload setting, or earth fault protection are required by an application.
The MCCB’s operating principle
When it comes to providing the overall trip mechanism that is relied on for protection and isolation, the MCCB system makes use of a temperature-sensitive device, also known as the thermal element, and a current-sensitive electromagnetic device, also known as the magnetic element. The thermal element and the magnetic element are both temperature-sensitive devices.
To provide protection and isolation, the MCCB device primarily makes use of a temperature-sensitive device known as the thermal element in conjunction with a current-sensitive device known as the magnetic elements. This allows the MCCB device to provide overload protection as well as electrical fault protection from any type of short circuit situations, as well as an electrical switch for immediate disconnection.
In other words, the MCCB is an option to a fuse since it doesn’t need an alternate once an overload is noticed. Unlike a fuse, this circuit breaker can be simply reset after a mistake and offers enhanced operator safety and ease without acquiring operating costs. Generally, these circuits have thermal current for over current and the magnetic element for short circuit release to work faster.
In essence, MCBs are smaller, more compact devices suitable for lower-power applications, while MCCBs are larger, more powerful devices designed for higher-power and more demanding industrial and commercial applications.



Hi, this is a comment.
To get started with moderating, editing, and deleting comments, please visit the Comments screen in the dashboard.
Commenter avatars come from Gravatar.